Shiseido reveals the possibility of controlling senescence of epidermal stem cells in collaborative research with CBRC
Shiseido has revealed through 5 years collaborative research with the Cutaneous Biology Research Center (CBRC) at Massachusetts General Hospital that phosphorylation of the RNA-binding protein YBX1, which suppresses epidermal stem cell senescence, reduces its function, thereby inducing cellular senescence. It has also demonstrated that the inhibition of YBX1 phosphorylation increases the number of epidermal stem cells, suggesting that in order to maintain the quantity of epidermal stem cells, the ”quality” of epidermal stem cells also is important. By applying these results, we aim to approach various skin aging-related issues via suppression of epidermal stem cell senescence.
The results of this study were presented in part at the International Societies of Investigative Dermatology Meeting, ISID 2023, held in Tokyo on May 10–13 by both sides of CBRC and Shiseido.
Research background
Skin turnover, which occurs as a result of cells in the epidermis constantly proliferating and differentiating, is important to maintain healthy skin. Epidermal stem cells are the sources of these cells and are found in the deepest part of the epidermis called basal layer. Shiseido has been engaged in epidermal stem cell research for 10 years, believing that it is very important to maintain healthy epidermal stem cells in order to realize youthful skin. As a result, we have discovered that supporting the maintenance of epidermal stem cells through the basement membrane, which lies beneath the basal layer of the epidermis, contributes to the retention of skin moisture and barrier function, and even the production of collagen in the dermis.
Our collaboration research partner, the team led by Associate Professor Anna Mandinova at CBRC, has revealed in their previous studies that a decrease in the level of the RNA-binding protein YBX1 leads to senescence of epidermal stem cells and also promotes the secretion of proteins that induce senescence of surrounding cells. In the present study, we took on the challenge of further advancing our stem cell research by focusing on the changes in the quality of epidermal stem cells as well as quantity.
Phosphorylation of YBX1 induces senescence of epidermal stem cells
In this study, Associate Professor Mandinova’s team at CBRC and Shiseido revealed that phosphorylated YBX1 observed in many of epidermal stem cells collected from donors of different ages showed reduced function. Moreover, when a drug that inhibits the phosphorylation of YBX1 was added to the cultured cells containing epidermal stem cells, and beta-galactosidase (beta-Gal), an indicator of cellular senescence, was stained, to compare their quantities, the results indicated a suppressing effect of the drug on cellular senescence.
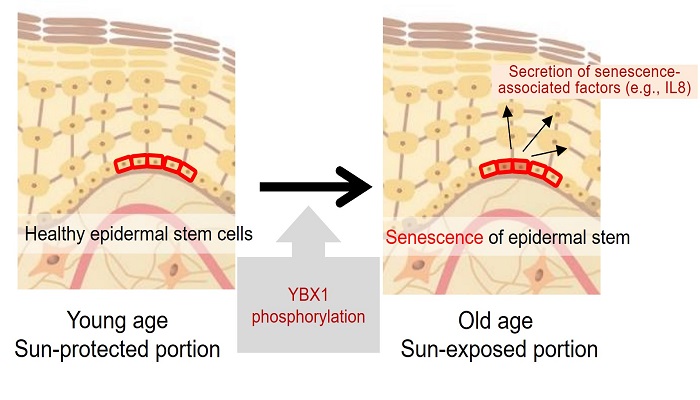
YBX1 phosphorylation occurs as a result of photoaging
In the real human skin, a decrease in YBX1-positive cells was observed with a reduction in epidermal stem cells due to aging or the influence of sunlight exposure. On the other hand, compared with the portion of the skin that was not exposed to sunlight (sun-protected portion), the part of the skin exposed to sunlight (sun-exposed portion) had a significantly increased level of phosphorylated YBX1. These results suggest that changes in the skin caused by exposure to sunlight over prolonged periods of time, i.e., photoaging, may be a factor contributing to YBX1 phosphorylation.
With the above discovery, it has become clear that the function of YBX1, an essential protein in the suppression of epidermal stem cell senescence, is reduced due to phosphorylation, and this, in turn promotes epidermal stem cell senescence. Shiseido believes that it is essential to maintain a healthy condition of epidermal stem cells, which are also the source of skin turnover to realize youthful skin. We will continue to advance epidermal stem cell research with the aim of developing approaches to addressing various skin concerns caused by aging.
Inhibition of YBX1 phosphorylation increases epidermal stem cells
It was found that when a piece of human skin was cultured with a drug that inhibits YBX1 phosphorylation, the number of epidermal stem cells increased.
With the above discovery, it has become clear that the function of YBX1, an essential protein in the suppression of epidermal stem cell senescence, is reduced due to phosphorylation, and this, in turn promotes epidermal stem cell senescence. Shiseido believes that it is essential to maintain a healthy condition of epidermal stem cells, which are also the source of skin turnover to realize youthful skin. We will continue to advance epidermal stem cell research with the aim of developing approaches to addressing various skin concerns caused by aging.
Source: Shiseido